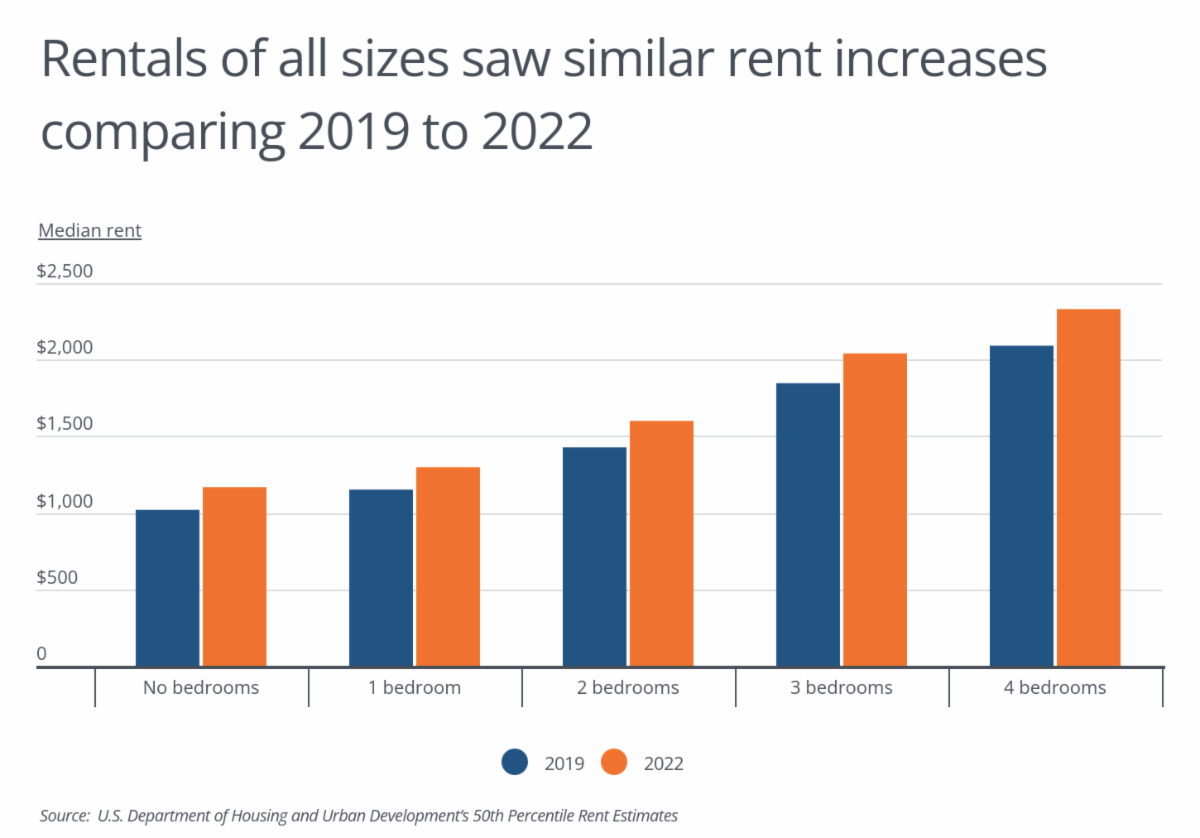
Georgia Sees 13.7% Increase in Median Rent, 12th Largest in U.S.
Monday, May 16th, 2022
Amid a historic run of inflation over the last year, the cost of housing—especially rent—has been one of the most significant pressures on household finances. Renters in many markets are seeing increases of 20% or more as they sign new leases, and with the nationwide rental vacancy rate at just 5.6%, renters have few alternatives to find more affordable options.
The current state of the rental market is a product of both supply and demand, with issues compiling over time and being exacerbated since the pandemic began. On the supply side, the U.S. has an estimated shortage of nearly 4 million housing units. Zoning and density restrictions have made it more difficult to add housing stock in many locations, both for rentals and in the real estate market. With rising real estate prices, 70% of the growth of the rental market since 2009 has come from higher-income earners who might otherwise have bought a home. And as more high earners enter or stay in the rental market, builders and developers are incentivized to provide more luxury units, which means less new stock to meet the needs of low- and middle-income earners.
The COVID-era economy has worsened all of these issues. The spike in home values and now rising interest rates are putting homeownership further out of reach for many would-be buyers, keeping more people in the rental market. Builders and developers are also struggling to keep up with heightened demand while managing costs. Ongoing supply chain challenges have made it more time-consuming and expensive to obtain building materials, while the tight labor market has left hundreds of thousands construction positions unfilled.
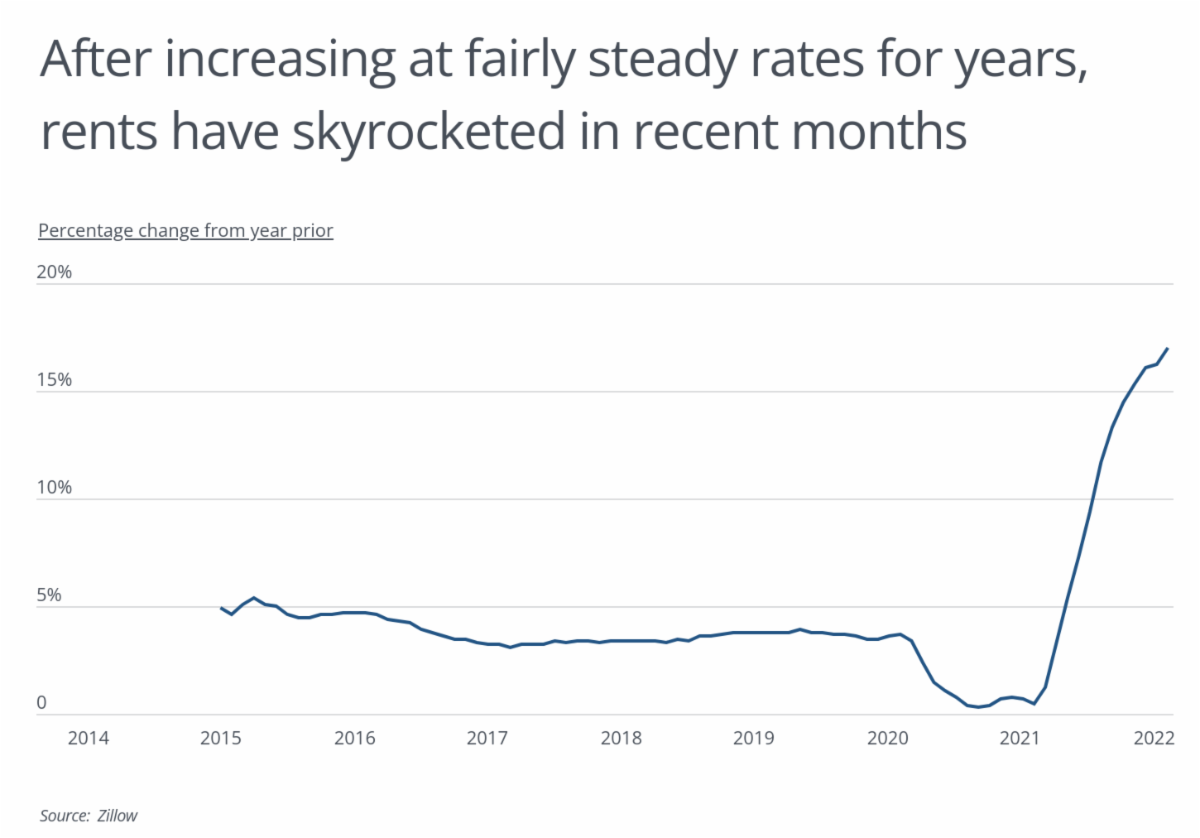 The last year has seen a dramatic spike in rental prices as a result of these factors, with a 17% year-over-year increase in rental costs from February 2021 to February 2022, according to data from Zillow. In comparison, the typical year-over-year increase has held steady between 3% and 5% for most of the last decade. And recent increases stand in stark contrast to the first year of the pandemic, when increases fell to less than 1% as landlords and renters navigated the economic uncertainty of the pandemic, and federal and state governments implemented rental assistance programs and eviction moratoriums to stabilize the market.
|